In this article, I will discuss effective strategies to fix Ethernet packet loss.
June 2024: Enhance your computer’s performance and eliminate errors with this cutting-edge optimization software. Download it at this link
- Click here to download and install the optimization software.
- Initiate a comprehensive system scan.
- Allow the software to automatically fix and repair your system.
Common Causes of Packet Loss
One of the most common causes of packet loss is network congestion. When the network becomes overwhelmed with traffic, packets can be dropped, leading to packet loss.
Network interface controller: Another common cause of packet loss is a faulty network interface controller. If the NIC is not functioning properly, it can result in packets being lost during transmission.
Wireless interference: Wireless networks are susceptible to interference from other electronic devices, such as microwaves or cordless phones. This interference can lead to packet loss on a wireless network.
Router issues: Problems with the router, such as outdated firmware or configuration issues, can also cause packet loss. Make sure your router is up to date and properly configured to prevent packet loss.
It is essential to identify and address these common causes of packet loss to improve the overall performance and reliability of your Ethernet connection. By troubleshooting these issues, you can minimize packet loss and ensure a smoother network experience.
Inspecting and Repairing Ethernet Components
| Component | Potential Issue | Repair Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Ethernet Cable | Physical damage or wear and tear | Replace the Ethernet cable with a new one |
| Network Interface Card (NIC) | Outdated drivers or hardware malfunction | Update NIC drivers or replace the NIC |
| Router/Modem | Overheating or outdated firmware | Cool down the router/modem and update firmware |
| Switch | Configuration issues or hardware failure | Check switch settings and replace if necessary |
| Wall Jack | Loose connection or damage | Check the wall jack connection and repair if needed |
Updating Devices and Firmware
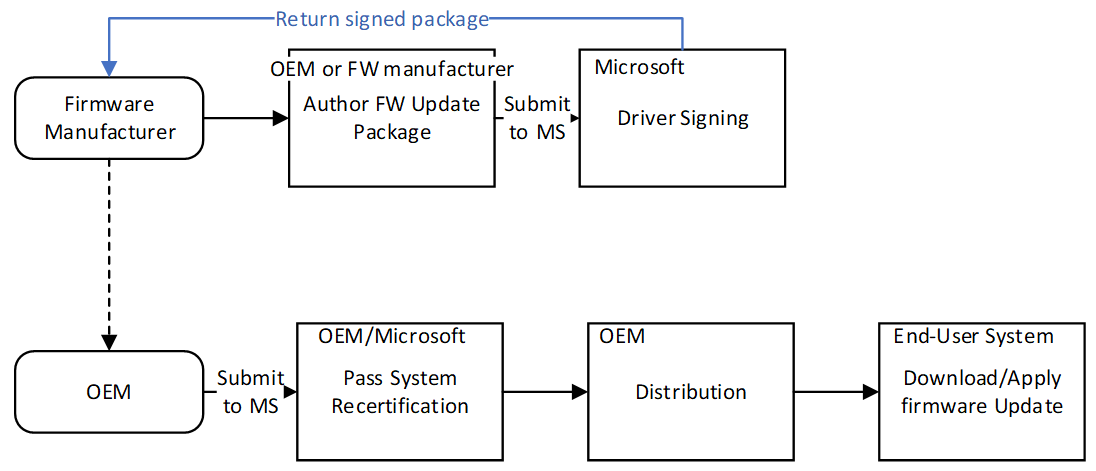
Regularly Update: Make it a habit to regularly check for updates for all your devices. New firmware releases often include bug fixes and performance improvements that can help reduce packet loss and improve network reliability.
Check Compatibility: Ensure that all devices on your network are compatible with each other. Incompatibility between devices can lead to packet loss and other network issues. If you suspect compatibility issues, consider upgrading to devices that are designed to work together seamlessly.
Monitor Performance: Use network monitoring tools to keep an eye on your network performance. Look for any spikes in latency or packet loss, which could indicate a problem with your network setup. Address these issues promptly to prevent further disruptions.
Seek Professional Help: If you continue to experience Ethernet packet loss despite updating devices and firmware, consider seeking help from a professional network technician. They can perform a thorough assessment of your network and recommend solutions to improve performance.
Strategies for Network Congestion

- Implement Quality of Service (QoS) settings:
- Access your router settings by typing the IP address into your browser.
- Locate the QoS settings and prioritize certain types of traffic over others.
- Upgrade your network equipment:
- Check for firmware updates for your router and install them if available.
- Consider upgrading to a router with better processing power and more advanced features.
- Optimize your network configuration:
- Use Ethernet cables instead of Wi-Fi for a more stable connection.
- Reduce the number of devices connected to your network to lessen congestion.
- Monitor network traffic:
- Use network monitoring tools to identify which devices or applications are causing congestion.
- Limit bandwidth usage for specific devices or applications if necessary.
Troubleshooting and Testing Your Connection
Troubleshooting: Start by checking all physical connections between your devices. Make sure Ethernet cables are securely plugged in, and there are no signs of damage.
Testing Your Connection: Use a network testing tool to check for packet loss. Ping your router to see if there are any issues with the connection.
Check for Interference: Make sure there are no sources of electromagnetic interference near your Ethernet cables, such as electrical cables or devices.
Update Drivers: Ensure that your network adapter drivers are up to date. Outdated drivers can cause connectivity issues and packet loss.
Consider Quality of Service: Adjust your router settings to prioritize Ethernet traffic over other types of data. This can help reduce packet loss during peak usage times.
Scan for Malware: Run a full system scan using antivirus software to check for any malware that may be affecting your network connection.
Consult with Your Internet Service Provider: If you continue to experience Ethernet packet loss, contact your ISP to see if there are any network issues on their end.
FAQs
How to fix packet loss in Ethernet?
To fix packet loss in Ethernet, you can start by rebooting your system and routers, checking network connections, using cable connections instead of Wi-Fi, updating software, replacing old hardware, configuring QoS settings, and strengthening security measures.
What is standard packet loss for Ethernet?
Standard packet loss for Ethernet is typically less than 1% or 0.1%, with certain applications like online gaming or VoIP requiring even lower rates for optimal performance.
What causes packet losses?
Packet losses are caused by a variety of factors including inadequate signal strength, interference, system noise, software corruption, overburdened network nodes, and network congestion.
Why am I getting packet burst with Ethernet?
You are experiencing packet burst with Ethernet likely due to network or server failures. This could be caused by an unstable or poor internet connection on your end, or matchmaking errors and distance from the game server on the server’s end.

