Are you experiencing a digital signature verification error on your Windows 7 computer? Let’s discuss how to fix this issue.
July 2025: Enhance your computer’s performance and eliminate errors with this cutting-edge optimization software. Download it at this link
- Click here to download and install the optimization software.
- Initiate a comprehensive system scan.
- Allow the software to automatically fix and repair your system.
Identifying Signature Errors
To identify signature errors in the article titled “Fix Windows 7 Digital Signature Verification Error,” follow these steps:
1. Check the digital signature of the file causing the error. Right-click on the file, select Properties, and go to the Digital Signatures tab. Look for any warnings or errors in the signature.
2. Verify the certificate used to sign the file. Click on the Details button in the Digital Signatures tab and check the certificate information. Look for any issues with the certificate chain or expiration date.
3. Use a trusted third-party tool to validate the digital signature. There are various tools available online that can help you verify the authenticity of the signature and identify any errors.
Updating Certificate Authorities
| Certificate Authority | URL |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Root Certificate Authority | https://www.microsoft.com/pki/certs/MicRooCerAut_2011-03-22.crt |
| VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority – G5 | https://www.verisign.com/repository/rootcertificates/VeriSign-Class%203-Public-Primary-Certification-Authority-G5.crt |
| GlobalSign Root CA | https://secure.globalsign.com/cacert/Root-R1.crt |
Configuring System Settings
To configure system settings in Windows 7 to fix the digital signature verification error, follow these steps:
1. Access the Control Panel by clicking on the Start button and selecting Control Panel from the menu.
2. In the Control Panel, navigate to System and Security and then click on System.
3. In the System window, click on Advanced system settings on the left-hand side.
4. In the System Properties window, go to the Hardware tab and click on Device Installation Settings.
5. Select the option to “Never install driver software from Windows Update” and then click Save Changes.
6. Restart your computer to apply the changes.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
-
Reboot Your System:
- Restart your computer to see if the issue resolves itself.
-
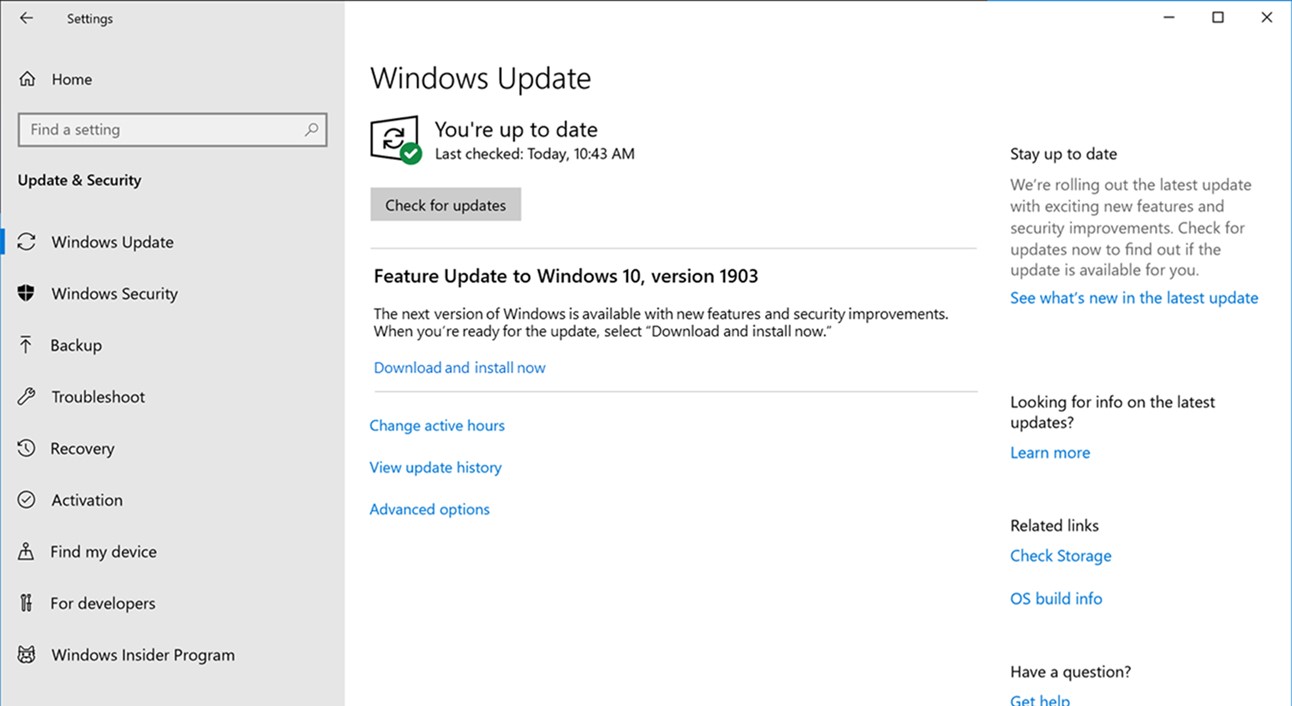
Update Windows:
- Go to the Control Panel.
- Click on Windows Update.
- Select Check for Updates.
- Install any available updates.
-
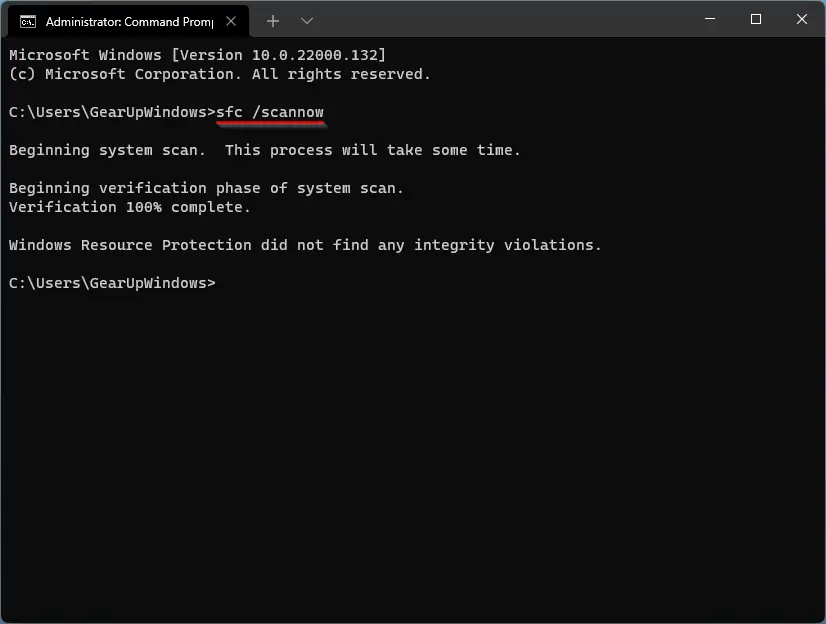
Run System File Checker:
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type sfc /scannow and press Enter.
- Wait for the scan to complete and follow any repair instructions.
-
Disable Driver Signature Enforcement:
- Restart your computer and press F8 during boot.
- Select Disable Driver Signature Enforcement.
- Continue booting into Windows.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I fix a digital signature error in Windows 7?
To fix a digital signature error in Windows 7, you can modify the Windows registry, update or uninstall the problematic driver, use the System File Checker utility, scan for file system errors, disable integrity checks, disable driver signature enforcement, or perform a system restore.
How do I bypass the digital signature on Windows 7?
To bypass the digital signature on Windows 7, you can disable driver signature enforcement by accessing the Advanced Boot Options menu and selecting the appropriate option.
How to fix this driver is not digitally signed in Windows 7?
To fix the “driver is not digitally signed” issue in Windows 7, you can disable the signature requirement by accessing the Start-Up Settings through the Troubleshoot menu.
How to solve digital signature problem?
To solve the digital signature problem, verify that the server is started on the correct port and ensure it matches the emSigner port description. Check the version of emSigner in Control Panel > Program and Features – uninstall version 1.2 and install emSigner v2 if necessary.